Modeling Time Series Data
The data model for TempoDB is centered around the concept of a Series. A Series is a sequence of timestamp/value pairs for a single source of measurement data.
Consider the imaginary thermostat below. Let's say it is measuring Temperature, Solar Radiation, and Humidity every 10 seconds.
That would equate to three different Series in TempoDB.

And since these three Series originate from the same thermostat, it would be useful to relate these Series to each other so you can find them easily when querying. This is done by adding metadata to each Series in the form of tags and attributes.
A tag is a string, and a Series can have a list of tags. An attribute is a key-value pair (both strings), and a Series can have many attributes (like a dictionary or hash).
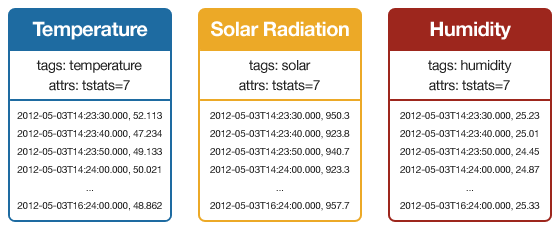
This allows you to make queries like: find all the Series associated with Thermostat 7. Using the Python client, that would look like:
client.get_series(attributes={"tstat": "7"})
and if you wanted to read time series data for those Series:
client.read(start, end, attributes={"tstat": "7"})
Or you could say: find all the humidity Series across all Thermostats.
client.read(start, end, tags=["humidity"])
The tagging and attribute system is simple and very powerful, and allows you to express queries of varying complexity.
To recap: a Series is a sequence of timestamp/value pairs for a single source of measurement data. You can relate Series to each other by using tags and attributes. To learn more, check out the Series API docs, or drop us an email [email protected].
